The Hijri Calendar: A Historical Journey Through Time
Related Articles: The Hijri Calendar: A Historical Journey Through Time
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Hijri Calendar: A Historical Journey Through Time. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Hijri Calendar: A Historical Journey Through Time
The Hijri calendar, also known as the Islamic calendar, is a lunar calendar used by Muslims worldwide to mark significant religious events and dates. Unlike the Gregorian calendar, which is solar-based, the Hijri calendar is based on the cycles of the moon, making it a purely lunar calendar.
Origins and Significance:
The Hijri calendar traces its origins to the year 622 CE, marking the pivotal moment in Islamic history when the Prophet Muhammad (peace be upon him) and his followers migrated from Mecca to Medina. This event, known as the Hijra, became the defining point for the establishment of the Islamic community and the birth of the Islamic calendar.
Lunar Cycles and Calendar Structure:
The Hijri calendar operates on a 12-month cycle, with each month determined by the sighting of the new moon. The lunar cycle, approximately 29.5 days long, dictates the duration of each month. This results in a Hijri year being approximately 11 days shorter than a Gregorian year.
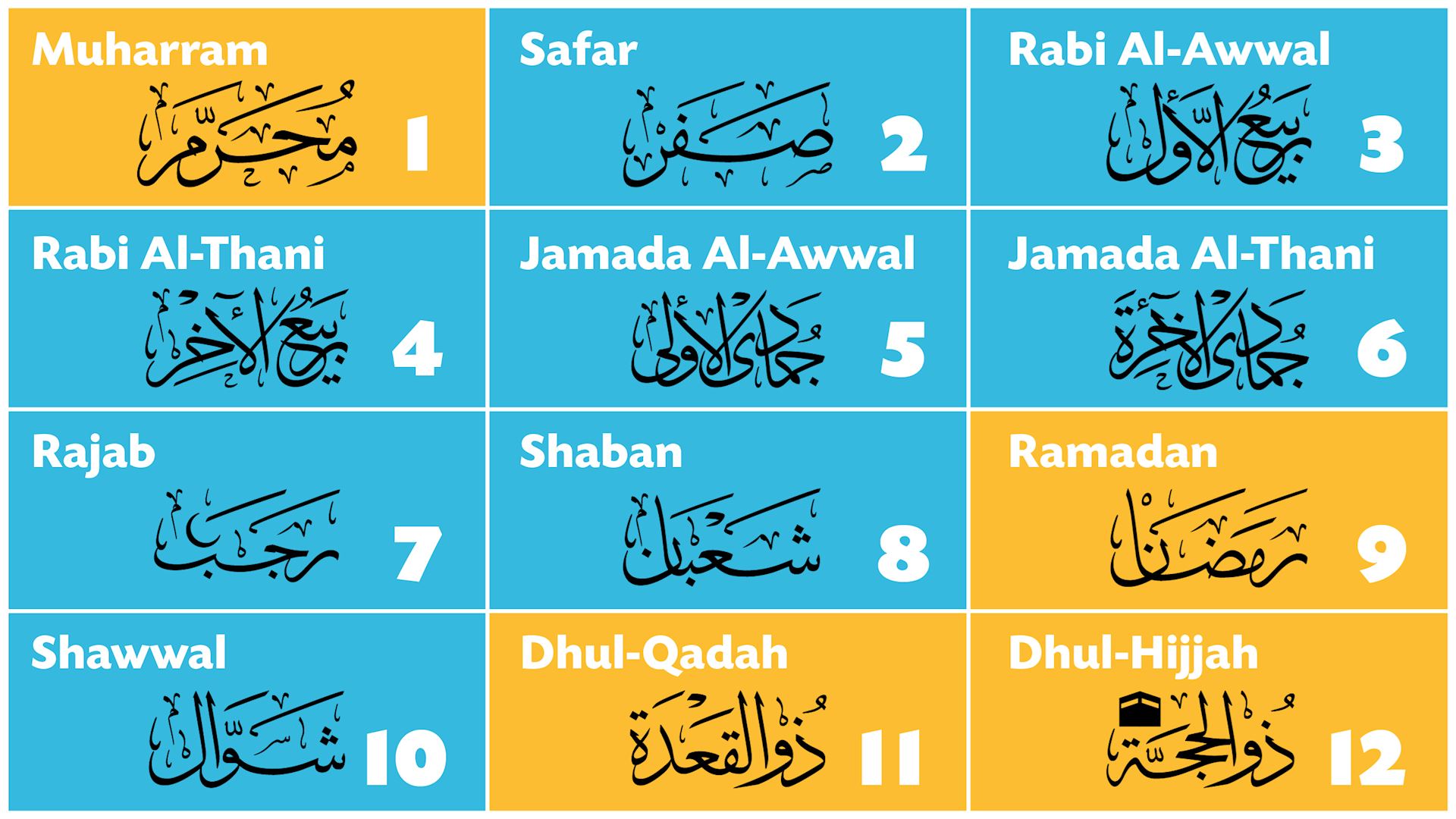
The months of the Hijri calendar are:
- Muharram: The first month of the Hijri calendar, often associated with the Day of Ashura, a day of mourning for the martyrdom of Imam Hussain.
- Safar: The second month, often considered a time of travel and change.
- Rabi’ al-Awwal: The third month, notable for the birthday of Prophet Muhammad (peace be upon him).
- Rabi’ al-Thani: The fourth month, often associated with the birth of Imam Ali (peace be upon him).
- Jumada al-Ula: The fifth month, marking the beginning of the winter season.
- Jumada al-Thaniyah: The sixth month, a period of reflection and preparation for the coming month of Ramadan.
- Rajab: The seventh month, a month of pilgrimage and spiritual retreat.
- Sha’ban: The eighth month, often associated with the Night of the Middle of Sha’ban, a night of prayer and seeking forgiveness.
- Ramadan: The ninth month, the holiest month in the Islamic calendar, during which Muslims fast from dawn till dusk.
- Shawwal: The tenth month, marked by the celebration of Eid al-Fitr, the festival that marks the end of Ramadan.
- Dhu al-Qa’dah: The eleventh month, a period of preparation for the pilgrimage to Mecca.
- Dhu al-Hijjah: The twelfth month, the most sacred month of the Hijri year, during which Muslims perform the Hajj pilgrimage and celebrate Eid al-Adha, the festival of sacrifice.
Importance and Significance:
The Hijri calendar holds immense religious and cultural significance for Muslims. It serves as a constant reminder of the events that shaped Islamic history and the core values of Islam. The calendar also plays a crucial role in regulating religious practices, including daily prayers, fasting during Ramadan, and the performance of Hajj.
Furthermore, the Hijri calendar is a symbol of Islamic unity, connecting Muslims worldwide through shared rituals and celebrations. The calendar fosters a sense of community and strengthens the bond between Muslims across different cultures and geographical locations.
Benefits of the Hijri Calendar:
The Hijri calendar offers several benefits, including:
- Religious Guidance: It provides a framework for observing religious obligations and rituals.
- Historical Awareness: It serves as a tangible connection to the past, reminding Muslims of the key events that shaped their faith.
- Cultural Unity: It promotes a sense of shared identity and fosters unity among Muslims globally.
- Time Management: The lunar nature of the calendar helps individuals become attuned to the cycles of nature and manage their time effectively.
The Hijri Calendar and Modernity:
In the modern world, the Hijri calendar coexists with the Gregorian calendar. While the Gregorian calendar is used for administrative and secular purposes, the Hijri calendar remains central to the lives of Muslims, marking religious events, festivals, and holidays.
The Hijri calendar has also been incorporated into various aspects of modern life, including:
- Education: Schools and universities often include courses on Islamic history and the Hijri calendar.
- Media: News outlets and media platforms report on Islamic events and holidays based on the Hijri calendar.
- Technology: Mobile apps and online calendars provide Hijri date conversions and reminders for Islamic events.
FAQs about the Hijri Calendar:
Q: How does the Hijri calendar differ from the Gregorian calendar?
A: The Hijri calendar is a lunar calendar, meaning it is based on the cycles of the moon, while the Gregorian calendar is a solar calendar, based on the earth’s orbit around the sun. This difference leads to a shorter Hijri year compared to a Gregorian year.
Q: What is the significance of the Hijra in the Hijri calendar?
A: The Hijra, the migration of Prophet Muhammad (peace be upon him) from Mecca to Medina, marks the beginning of the Hijri calendar. It is considered a pivotal event in Islamic history, signifying the establishment of the Islamic community and the birth of the Islamic calendar.
Q: How are the months of the Hijri calendar determined?
A: Each month in the Hijri calendar is determined by the sighting of the new moon. When the new moon is sighted, the previous month ends, and a new month begins.
Q: What are the most important religious events in the Hijri calendar?
A: Some of the most important religious events in the Hijri calendar include:
- Ramadan: The ninth month, during which Muslims fast from dawn till dusk.
- Eid al-Fitr: The festival that marks the end of Ramadan.
- Hajj: The pilgrimage to Mecca, performed during the month of Dhu al-Hijjah.
- Eid al-Adha: The festival of sacrifice, celebrated on the 10th day of Dhu al-Hijjah.
Q: How can I convert a Gregorian date to a Hijri date?
A: Several online tools and apps are available to convert Gregorian dates to Hijri dates. You can also find Hijri date converters in many Islamic websites and mobile apps.
Tips for Understanding and Using the Hijri Calendar:
- Learn the names of the months: Familiarize yourself with the names of the Hijri months and their significance.
- Mark important dates: Use a Hijri calendar to mark important religious events and holidays.
- Attend religious gatherings: Participate in religious gatherings and celebrations that occur during the Hijri year.
- Learn about Islamic history: Explore the history of the Hijri calendar and its role in shaping Islamic culture and civilization.
Conclusion:
The Hijri calendar is an integral part of Islamic culture and practice. It serves as a historical reminder of the pivotal events that shaped the faith, guides religious observances, and fosters a sense of unity among Muslims worldwide. Understanding the Hijri calendar provides valuable insights into Islamic history, culture, and the spiritual journey of Muslims. By embracing the Hijri calendar, individuals can deepen their connection to their faith and appreciate the richness and diversity of Islamic traditions.






.png)

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Hijri Calendar: A Historical Journey Through Time. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!